DO THEY SEE WHAT WE SEE?
by: LAION, 19 Jun, 2025
Building Emotionally Intelligent AI with EmoNet, a suite of open tools and resources developed by the LAION community
A LAION & Intel Collaboration
Authors
LAION e.V.
Christoph Schuhmann*, Robert Kaczmarczyk*, Gollam Rabby, Felix Friedrich, Maurice Kraus, Kourosh Nadi, Desmond Grealy, Huu Nguyen, Cahya Wirawan, Krishna Kalyan, Kristian Kersting, Sören Auer
Intel Corporation
Jayaraman Mahalingam
An exciting frontier in technology today is the quest for artificial intelligence that truly understands and interacts with humans on a deeper level. While AI has made remarkable progress in language processing and complex problem-solving, one critical dimension has yet to be fully realized: true emotional intelligence.
Can our AI systems perceive the subtle joy in a crinkled eye, the faint tremor of anxiety in a voice, or the complex blend of emotions that color our everyday interactions? We believe this is not just a fascinating academic pursuit but a fundamental necessity for the future of human-AI collaboration.
Today, we're proud to release EmoNet – a suite of new, open and freely available models and tools designed to support global research and innovation in the emerging field of emotionally intelligent AI. Our contributions are multi-faceted, addressing critical gaps in current research and providing powerful new tools for the global AI community.
Thank you to our partner Intel. LAION and Intel have been collaborating on fostering empathic, thoughtful and productive human-AI interaction for several years.
Voice Acting Samples Demo
Our Empathic Computing Contributions
1. EMONET-FACE Benchmark
A novel, expert-annotated benchmark for fine-grained facial emotion estimation, featuring a comprehensive 40-category emotion taxonomy and large-scale, demographically diverse synthetic image datasets (EMONET-FACE BIG, BINARY, and HQ).
📊 Dataset: EMONET-FACE hosted by Hugging Face

Figure 2: Samples from our EmoNet-Face datasets generated with different SOTA T2I models.
2. EMONET-VOICE Benchmark
A similarly fine-grained, expert-verified benchmark for speech emotion detection. Built upon our 40-category taxonomy and leveraging state-of-the-art synthetic voice generation for privacy and diversity. It includes 4,692 high-agreement audio samples.
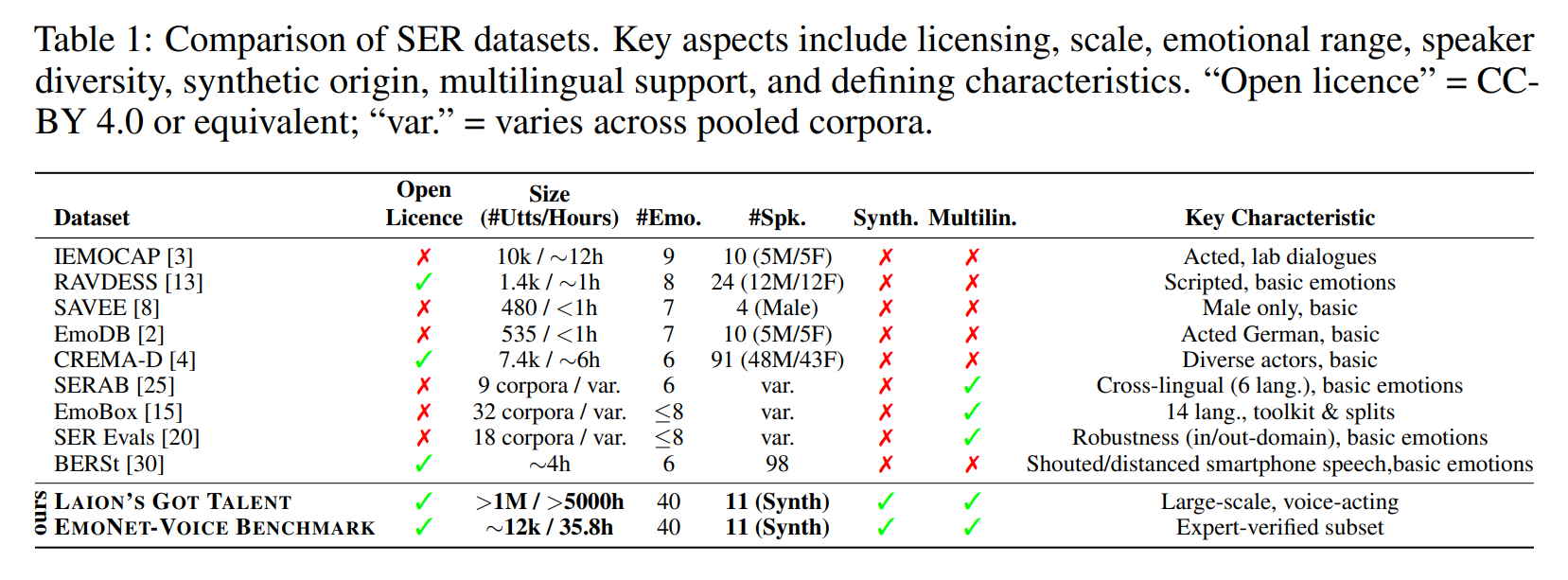
Table 1: Comparison of SER datasets. Key aspects include licensing, scale, emotional range, speaker diversity, synthetic origin, multilingual support and defining characteristics.
3. EMPATHIC INSIGHT-FACE Model
A state-of-the-art model for facial emotion estimation trained on our EMONET-FACE suite, surpassing the performance of leading models like Gemini 2.5 Pro and proprietary APIs like Hume AI on our benchmarks.
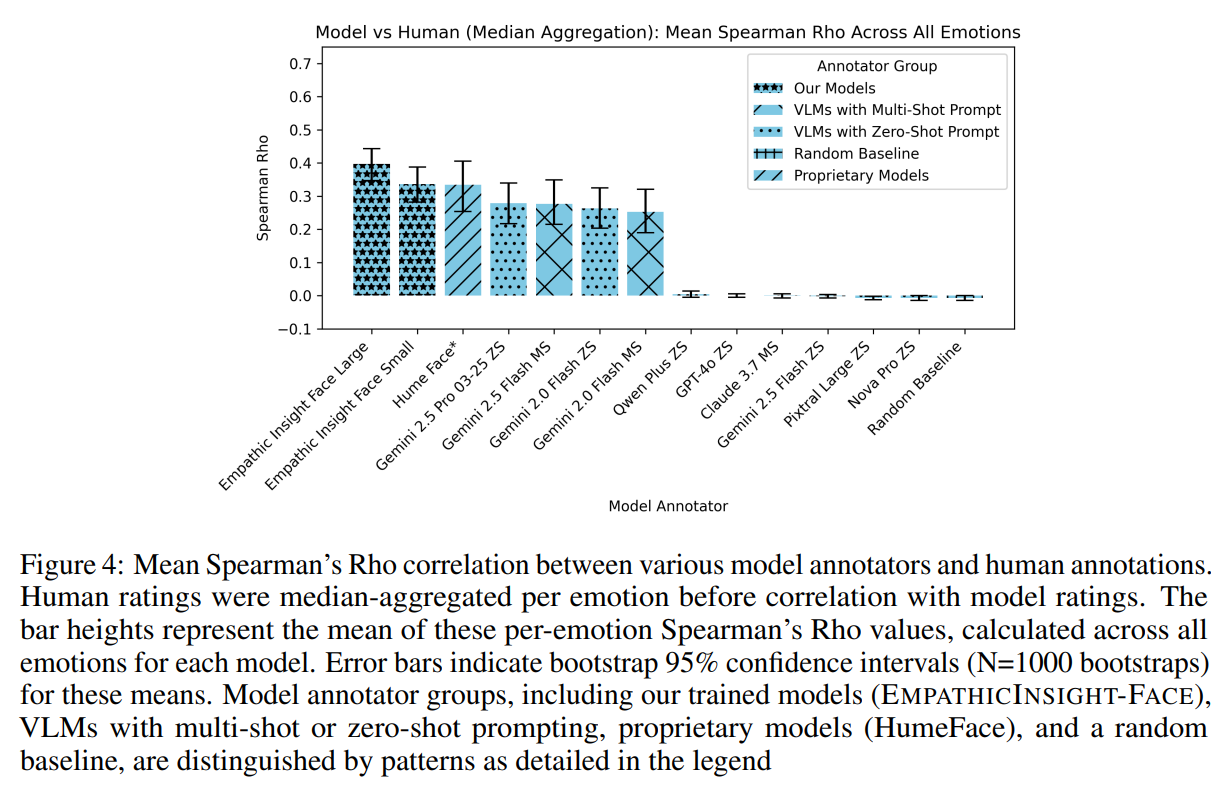
Figure 3: Mean Spearman's Rho correlation between various model annotators and human annotations.
This figure highlights the strength of facial emotion recognition correlation between the EmoNet Empathic Insights models and actual emotions compared to other models. The bar heights represent the mean of these per-emotion Spearman's Rho values calculated across all emotions for each model. Error bars indicate bootstrap 95% confidence intervals (N=1000 bootstraps) for these means. Model annotator groups, including our trained models (Empathic-Insight-Face), VLMs with multi-shot or zero-shot prompting, proprietary models (HumeFace), and a random baseline, are distinguished by patterns as detailed in the legend.
🔗 Models:
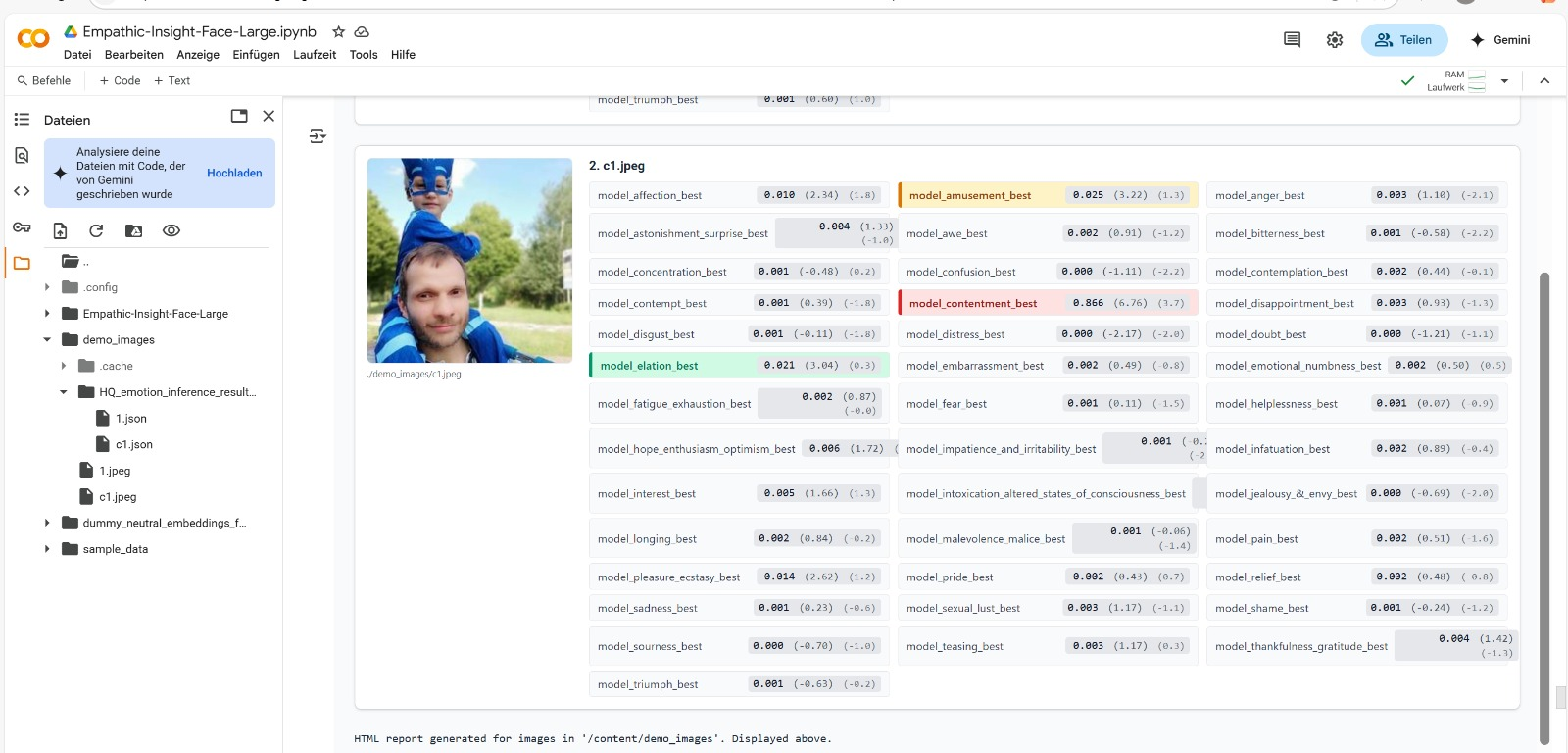
Figure 4: EMPATHIC INSIGHT-FACE Model prediction example
💻 Try it: EMPATHIC INSIGHT-FACE Model Colab
4. EMPATHIC INSIGHT-VOICE Model
A state-of-the-art model for speech emotion estimation, setting a new benchmark for nuanced understanding of vocal emotional cues, similarly outperforming established systems on our EMONET-VOICE benchmark.
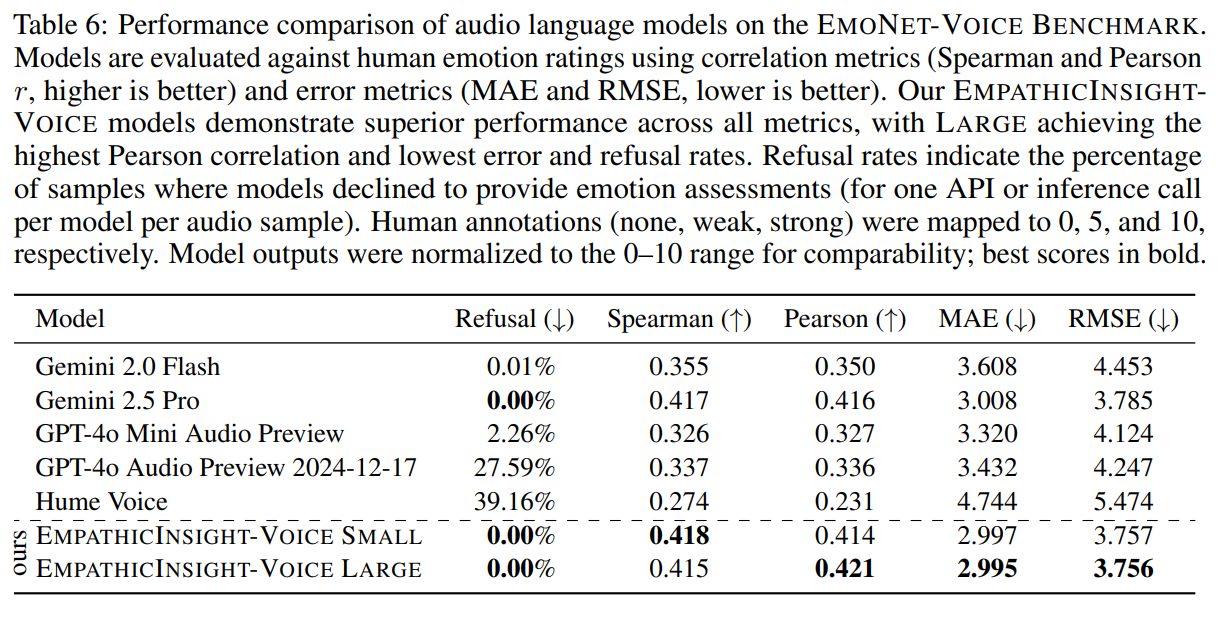
Table 2: Performance Comparison of Audio Language Models on the EmoNet-Voice Benchmark.
🔗 Models:
5. BUD-E Whisper (Better Understanding of Emotion Whisper)
A suite of fine-tuned Whisper models for advanced emotional speech captioning, going beyond mere transcription to describe emotional tone, vocal bursts, and speaker traits.
🔗 Resources:
6. LAION's Got Talent Dataset
An extensive synthetic voice-acting dataset, forming the foundation for EMONET-VOICE, featuring over 5,000 hours of speech across 11 synthetic voices, 40 emotions, and 4 languages. The cumulative playtime of this dataset is more than the cumulative playtime of all movies shown in US cinemas from 2021 to 2024, putting its sheer scale into perspective.
📊 Datasets:
Introducing EMONET-FACE & EMONET-VOICE: A New Foundation
To address these challenges, we developed the EMONET suites. At their core is a novel 40-category emotion taxonomy, meticulously derived from an extensive analysis of the "Handbook of Emotions" and refined through consultation with psychologists. This taxonomy moves far beyond basic emotions, encompassing a rich spectrum of positive and negative affective states, cognitive states (e.g., Concentration, Confusion, Doubt), physical states (e.g., Pain, Fatigue, Intoxication), and socially mediated emotions (e.g., Embarrassment, Shame, Pride, Teasing). This granularity is crucial for building AI that can appreciate the finer details of human emotional life.
EMONET-FACE
EMONET-FACE provides a rich resource for visual emotion understanding:
- EMONET-FACE BIG (over 203,000 synthetic images) offers a vast dataset for pre-training models.
- EMONET-FACE BINARY (approx. 20,000 images) is designed for fine-tuning and features over 62,000 binary (present/absent) emotion annotations from human experts. These annotations underwent a rigorous multi-stage process, requiring triple positive agreement for affirmative labels and a contrastive batch to ensure high-quality true negatives.
- EMONET-FACE HQ (2,500 images) serves as our gold-standard evaluation benchmark. Each image was meticulously rated by multiple psychology experts on a continuous 0-7 intensity scale across all 40 emotion categories, resulting in 10,000 expert annotations.
The synthetic images were generated using state-of-the-art text-to-image models with explicit prompts to ensure diverse demographic representation (across ethnicity, age, and gender) and clear, full-face expressions. This approach not only allows for controlled diversity but also sidesteps the ethical concerns associated with using real individuals' images.
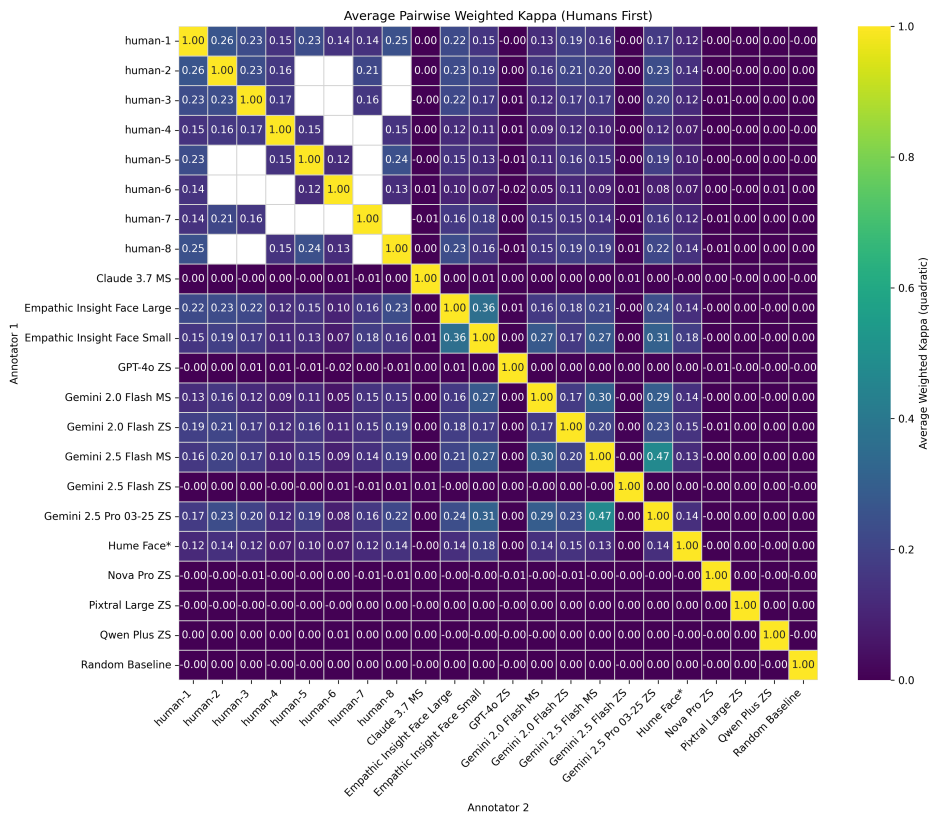
Figure 5: Mapping Facial Expression Emotional Understanding
EMONET-VOICE
EMONET-VOICE tackles the auditory domain with similar rigor:
- EMONET-VOICE curates 4,692 high-agreement audio samples from LAION's Got Talent.
- Each snippet simulates actors portraying scenes designed to evoke specific emotions.
- Crucially, each snippet underwent rigorous validation by human experts with psychology degrees. They assigned perceived intensity labels (Not Present, Mildly Present, Intensely Present) based on a strict 3-annotator consensus protocol, focusing on estimating the presence and intensity of emotions rather than assuming a single definitive label.
This privacy-preserving approach allows for the inclusion of sensitive emotional states often absent in existing datasets.
Why Emotion in Speech and Face Matters: The Vision of Universal Voice Actors
Effective communication transcends mere words. It's woven with the rich threads of emotion, conveyed through the subtle shifts in our facial expressions and the intricate nuances of our voice. Capturing these expressions enables AI assistants to become more empathetic, engaging, and supportive; qualities crucial for transformative applications in education, mental health, companionship, and beyond.
We envision a future where multimodal foundation models evolve into "omni-models" with sophisticated audio-in/audio-out capabilities. Soon, every new foundation model on platforms like Hugging Face could be capable of performing voice acting like Robert De Niro or Scarlett Johansson. These AI systems will function like world-class voice actors, capable of being prompted not just by text, but also by voice, to adopt any persona. Imagine an AI that can embody an empathetic educator adapting to a student's confusion, a thrilling storyteller captivating an audience, or a knowledgeable research assistant explaining complex concepts with clarity and appropriate gravitas. This level of seamless and inspiring human-AI interaction is our ultimate goal.
The Imperative for Better Benchmarks: Seeing and Hearing the Nuance
The journey to emotionally intelligent AI begins with data. Existing datasets for emotion recognition, while valuable, often present significant limitations. Facial emotion datasets might rely on a narrow range of "basic" emotions, use images with occlusions or poor lighting, or lack demographic diversity, leading to biased models that perform poorly across different populations. Similarly, speech emotion datasets can be constrained by coarse emotion taxonomies, privacy concerns tied to real user data, or an over-reliance on acted portrayals that don't capture the subtlety of spontaneous emotional expression.
The Theory of Constructed Emotion (TCE), a prominent psychological framework (research link), posits that emotions are not universal, pre-programmed entities that we simply "recognize." Instead, they are constructed by our brains based on a combination of interoceptive signals (like valence – pleasantness/unpleasantness, and arousal – activation/deactivation), learned concepts, and contextual information. This means there isn't a single, definitive facial expression or vocal intonation for "joy" or "sadness" that is universally and unambiguously displayed. Rather, emotional expression is a complex, dynamic, and often ambiguous signal.
This understanding underscores the need for emotion estimation rather than simple recognition. We need AI that can assess the likelihood and intensity of various emotions being present, rather than forcing a single label onto a complex human state.
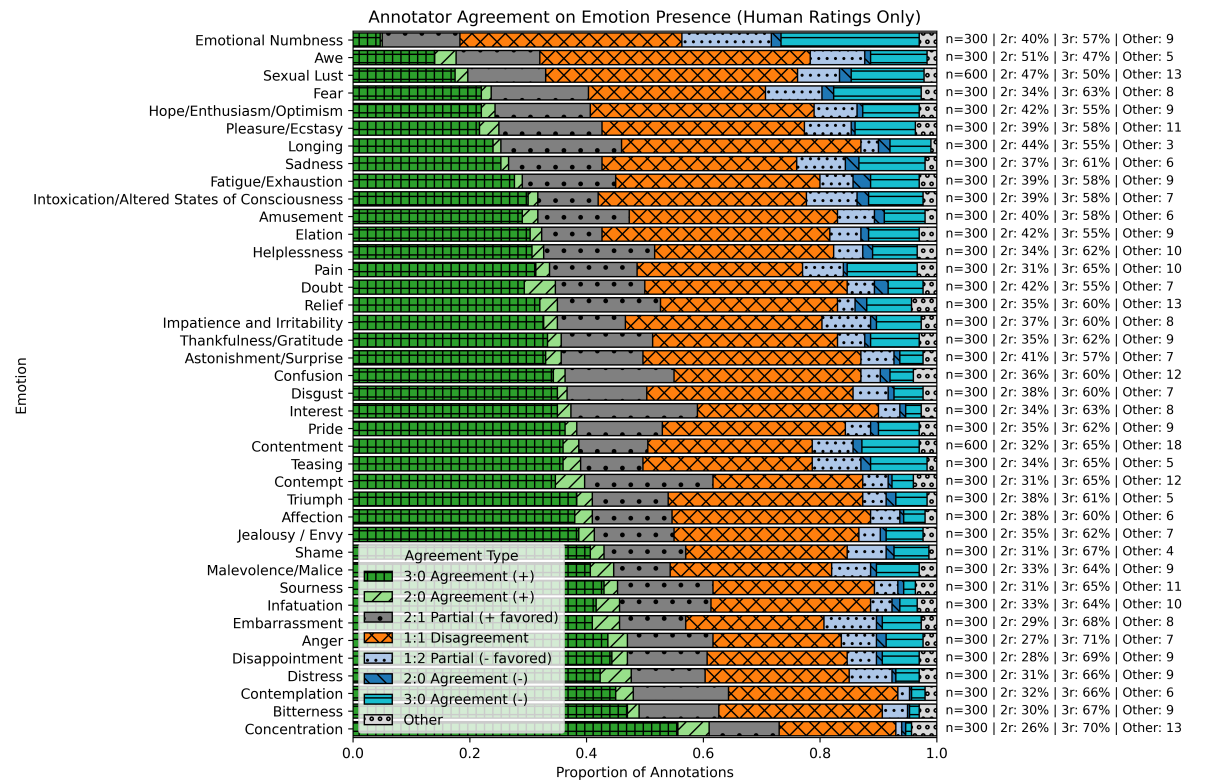
Figure 6: Mapping Voice Emotional Understanding
Motivation and Taxonomy Development: Capturing the Full Spectrum
Our approach to defining the emotional landscape for these datasets was systematic and grounded in psychological theory, while also addressing practical needs for AI applications:
- Theoretical Foundations & Gap Analysis: We analyzed established psychological frameworks, such as Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions. While foundational, these often neglect states critical for real-world AI, like Bitterness (often linked to social exclusion), physical states like Pain and Fatigue, or altered states like Intoxication. Though not always strictly classified as "emotions" in psychology, their accurate perception is vital for empathetic AI.
- "Handbook of Emotions" Extraction: We processed the comprehensive "Handbook of Emotions" (edited by Lisa Feldman Barrett et al.) in 500-word chunks, using a large language model (LLM) to extract emotion-related nouns and adjectives.
- Refinement to 40 Categories: After automatic clustering of these terms, manual refinement by our team, in consultation with psychology experts, yielded our final 40-category taxonomy. This taxonomy, shared by both EMONET-FACE and EMONET-VOICE, is detailed below.
Full Emotion Taxonomy
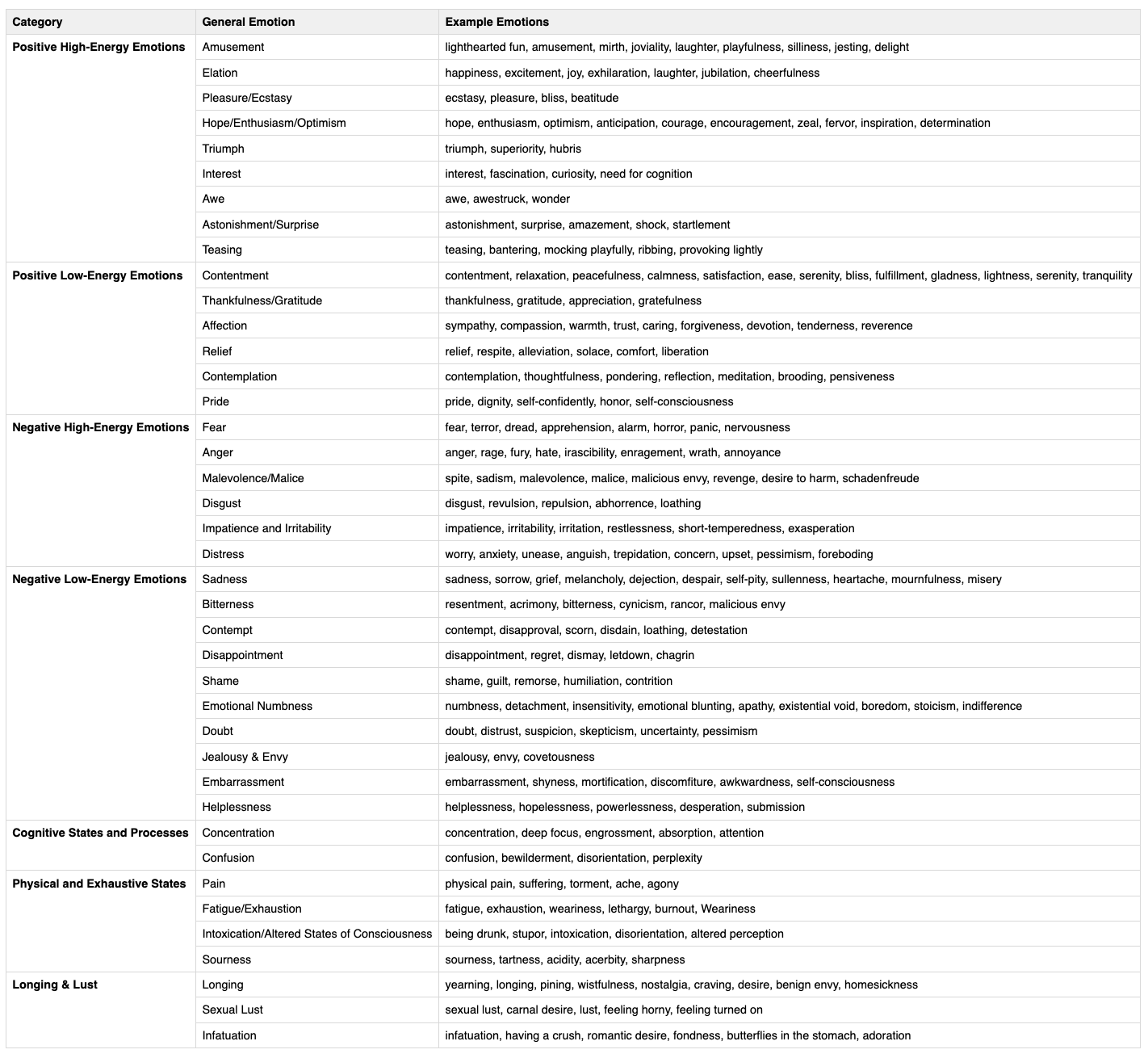
Table 3: Taxonomy Listing of Emotions Captured in Datasets
The EMONET-VOICE Benchmark: A Gold Standard for Speech Emotion
Leveraging the rich LAION's Got Talent dataset, we are establishing the EMONET-VOICE Benchmark. This isn't just another dataset; it's a meticulously curated training and evaluation corpus for our 40-category emotion taxonomy.
- Intensity Annotation: Each audio snippet is being annotated for emotional expression intensity. For most emotions, a three-level scale is used: non-existent, slightly expressed, and strongly/fully expressed. For certain high-intensity or inherently ambiguous categories, a two-level distinction (non-existent vs. present) is applied.
- Expert Psychological Annotators: To ensure the highest reliability, labeling is conducted by annotators with formal psychological training (typically at least a bachelor's degree).
- Strict Consensus Protocol: Only labels achieving exact agreement among three independent expert annotators (no disagreement on the intensity level) are included. This conservative approach ensures exceptional inter-rater reliability, making the annotations a true gold standard.
Unlike existing benchmarks often limited to basic emotions or binary states, EMONET-VOICE offers a structured, expert-validated evaluation across 40 nuanced categories, applicable to both naturalistic and synthetic speech. This will enable objective, reproducible, and fine-grained assessment of models like BUD-E Whisper and future multimodal systems.

EMONET-FACE: Paralleling Progress in Visual Emotion Recognition
Our efforts in speech emotion are mirrored by our work in facial emotion recognition with the EMONET-FACE suite. This includes:
- EMONET-FACE BIG: Over 203,000 synthetic images for pre-training.
- EMONET-FACE BINARY: Approx. 20,000 images with 65,000+ human expert binary emotion annotations for fine-tuning.
- EMONET-FACE HQ: 2,500 images with 10,000 continuous (0-7 scale) expert annotations across all 40 emotions for high-fidelity evaluation.
EMPATHIC INSIGHT Models: Setting New State-of-the-Art Performance
The power of these benchmarks is demonstrated by our EMPATHIC INSIGHT models, which showcase the capabilities unlocked by our datasets and taxonomies:
- EMPATHIC INSIGHT-FACE achieves human-expert-level performance on EMONET-FACE HQ, outperforming models like Gemini 2.5 Pro and proprietary APIs. (More technical details on the model architecture and training can be found in our accompanying paper/technical report).
- EMPATHIC INSIGHT-VOICE, trained on LAION's Got Talent and EMONET-VOICE, similarly sets a new SOTA for nuanced speech emotion estimation. (Further technical specifics on this model are also available).
These models, are permissively licensed (Creative Commons for the models, Apache 2.0 for the code), prove that with focused dataset construction and careful modeling, AI can indeed learn to "see" and "hear" emotions with a level of nuance approaching human perception.
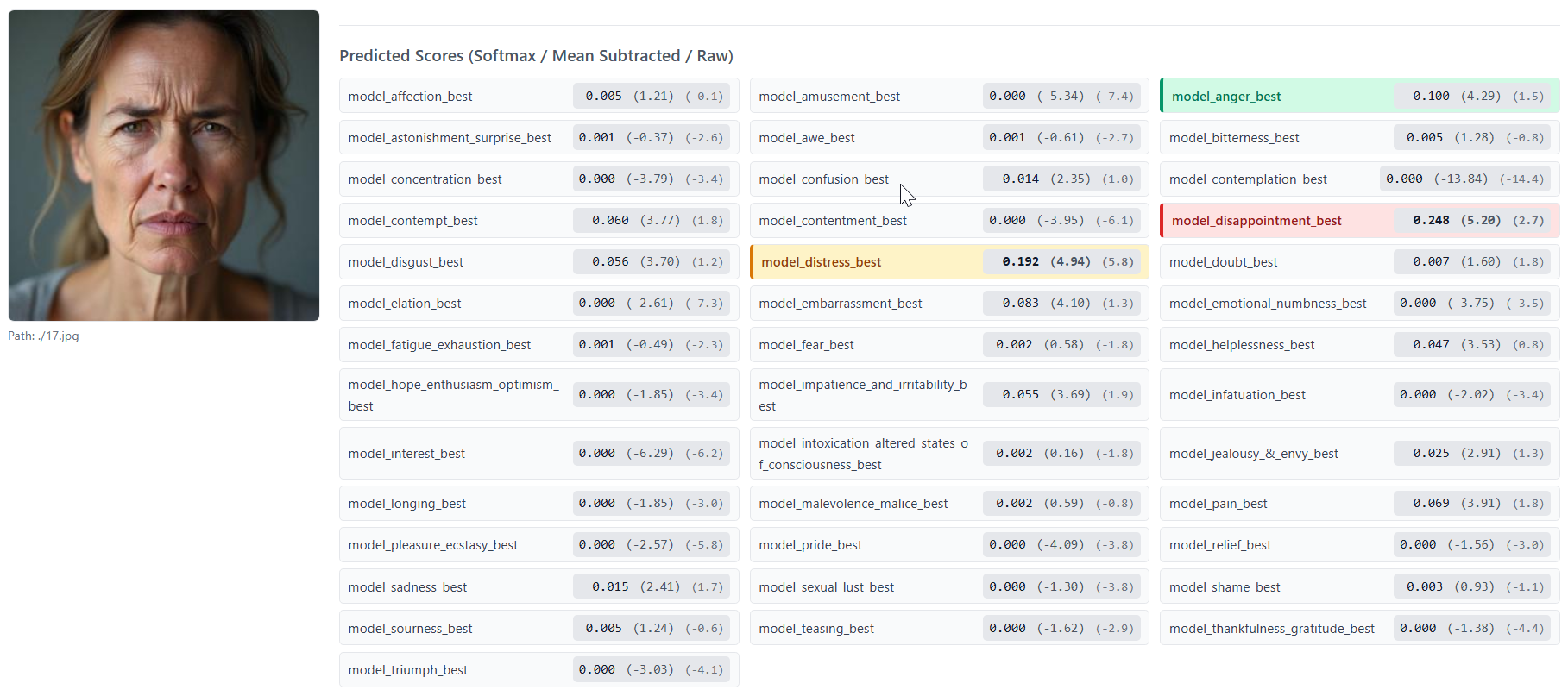
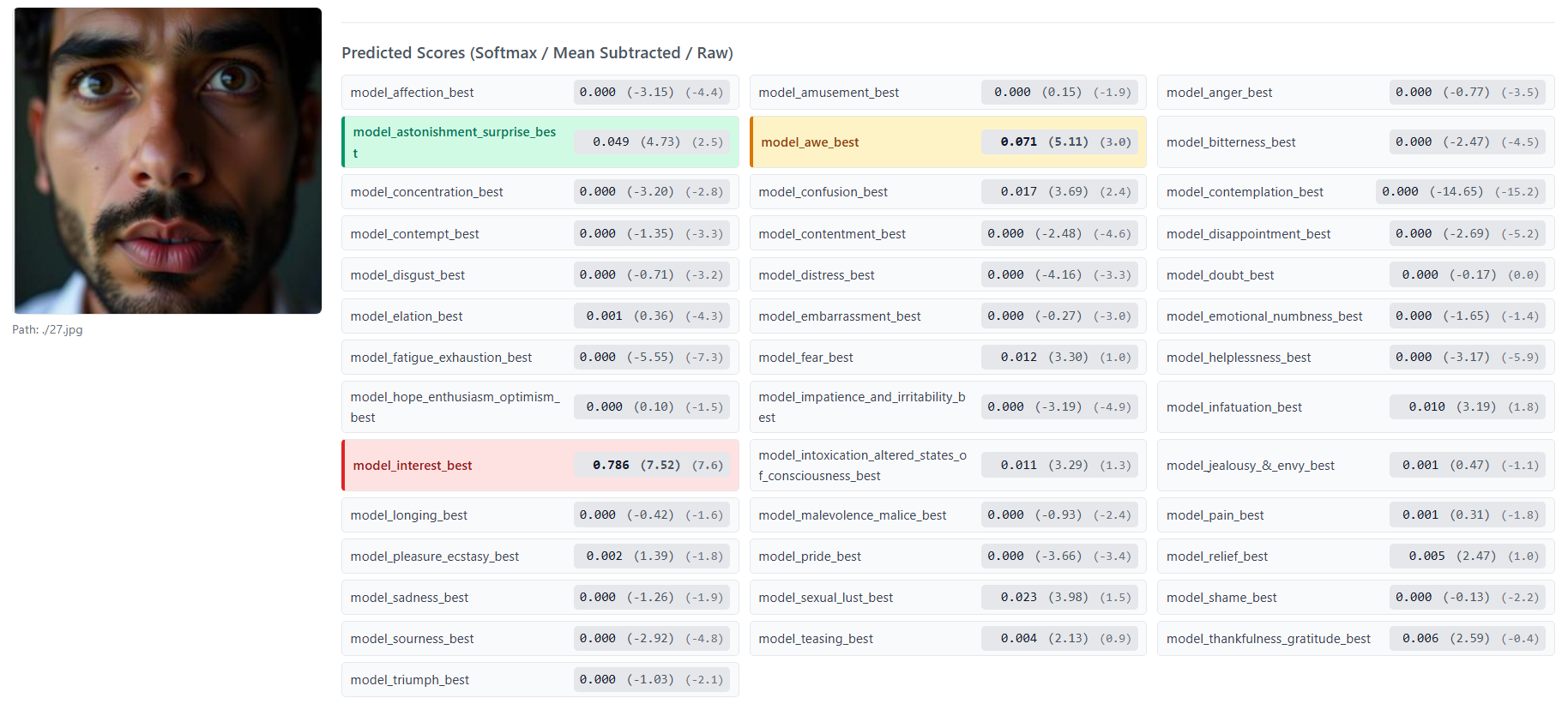
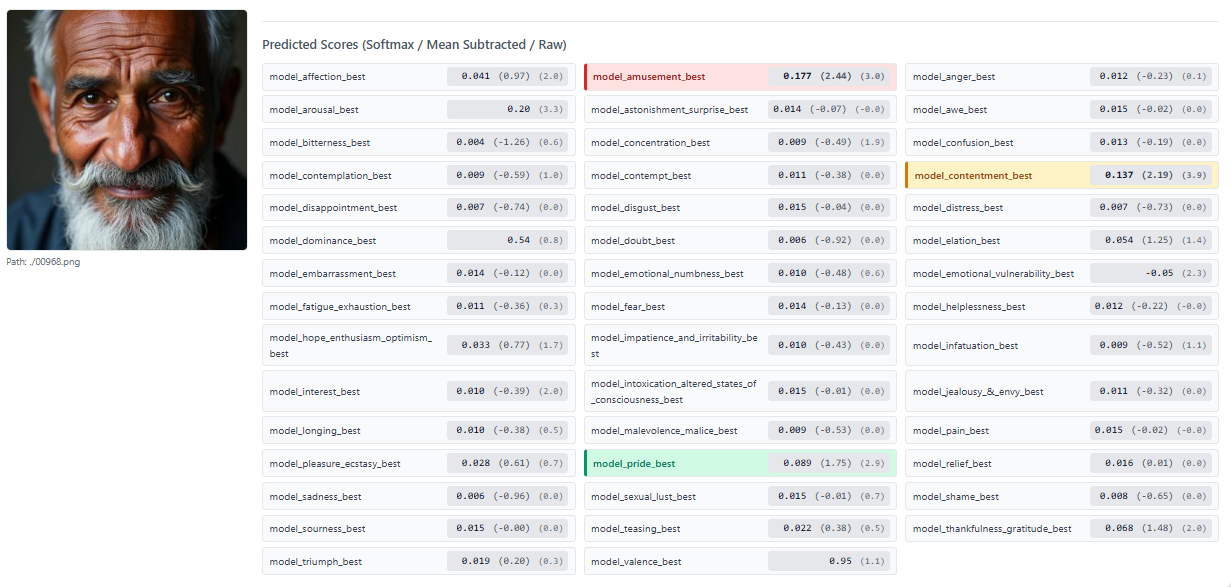
Figure 7: More EMPATHIC INSIGHT-FACE Model prediction examples
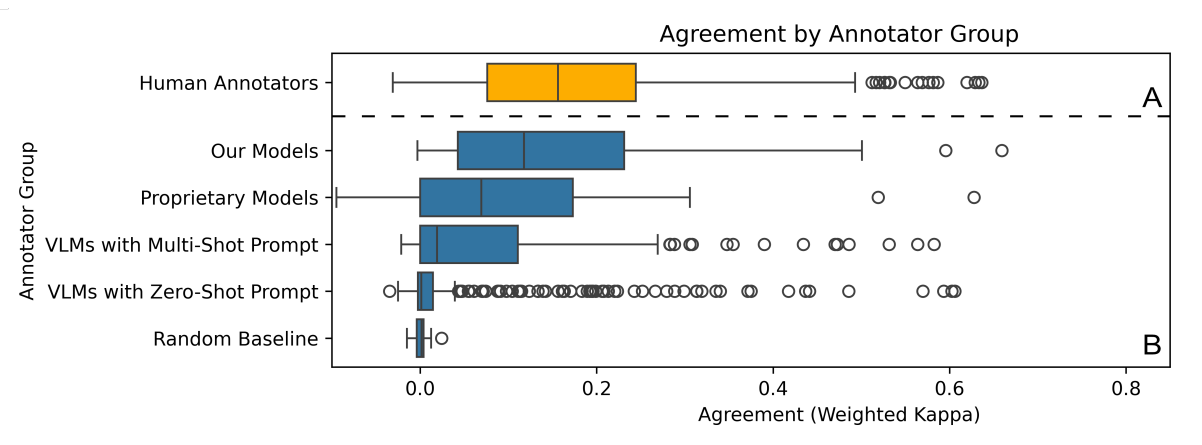
Figure 8: LAION's Empathic Insights Face Models Closely Track with Human Annotators
Introducing BUD-E Whisper: Beyond Transcription to Emotional Understanding
To truly unlock the emotional content within speech, transcription alone is insufficient. This led us to develop BUD-E Whisper, a suite of fine-tuned variants of OpenAI's Whisper model. BUD-E Whisper is specifically adapted for advanced emotion captioning. These models go beyond simply converting speech to text; they generate structured descriptions of:
- Emotional Tone: Identifying the perceived emotions from our 40-category taxonomy.
- Vocal Bursts: Recognizing non-lexical expressions like laughter, sighs, gasps, etc.
- Speaker Traits: Inferring characteristics like age, gender, and even speech style.
The training of BUD-E Whisper was a journey of iterative refinement. We utilized a diverse dataset including the LAION's Got Talent voice-acting data and approximately 5,000 hours of audio from public vlogs, online diaries, and cinematic dialogue, with Voice Activity Detection (VAD) used to isolate speech segments. Gemini Flash 2.0 was then employed to annotate these samples along our 40-category emotion taxonomy.
Initial experiments attempting direct regression from Whisper's architecture to scalar emotion intensity values (0-5 scale) proved challenging, as the autoregressive nature of Whisper isn't inherently suited for stable numerical output. We then shifted to a captioning approach. First, we used procedurally generated emotion summaries – templated sentences describing emotions, intensity, and speaker traits. While an improvement, these templates led to syntactic predictability and overfitting. The breakthrough came when we used LLMs to paraphrase these procedural captions. This introduced crucial syntactic variability while preserving semantic consistency. Training on these diverse, paraphrased captions enabled BUD-E Whisper to produce fluid, context-sensitive, and highly interpretable emotion descriptions.
The result is a robust system capable of identifying and describing nuanced emotional signals in speech, representing a significant step towards more emotionally aware voice assistants. BUD-E Whisper is particularly useful for generating rich captions for audio, preparing data for training text-to-speech and foundation models.
LAION's Got Talent: A Rich Tapestry of Synthetic Voices
At the heart of our speech emotion initiative is the LAION's Got Talent dataset. This comprehensive resource, created via the HyperLab API leveraging OpenAI's GPT-4 Audio model, comprises:
- 11 distinct voices: Offering a variety of vocal timbres and characteristics.
- 40 meticulously curated emotion categories: (Listed in detail above)
- Four languages: English (approx. 2,156 hours), German (approx. 716 hours), Spanish (approx. 888 hours), and French (approx. 881 hours).
- Acting Challenges (English + German): Approximately 111 hours of specialized scenarios.
- Diverse English Accent Distribution: Including Louisiana (~133h), Valley Girl (~159h), British (~132h), and even English spoken with simulated Chinese, French, German, Indian, Italian, Mexican, Russian, Spanish, and Texan accents, plus a "Vulgar Street English" category (~149h), and English without specific accent specified (~391h), ensuring a broad representation.
📊 Download the LAION's Got Talent Datasets:
The Power of Synthetic Data: Ethical and Diverse
A cornerstone of our initiative is the strategic use of synthetic data. This approach offers several key advantages:
- Privacy: It entirely bypasses the ethical complexities and privacy risks associated with collecting and annotating real human emotional expressions, especially for sensitive states.
- Diversity and Control: We can programmatically ensure demographic diversity in our datasets, controlling for age, gender, and ethnicity in facial images, and voice characteristics in speech. This is crucial for building fairer and less biased AI systems.
- Scale and Scope: Synthetic generation allows us to create datasets of a scale and emotional breadth that would be prohibitively expensive or logistically impossible to achieve with human-acted or in-the-wild data.
Investing in Open Standards-based AI Innovation
Intel is excited to collaborate with AI innovators like LAION, setting the groundwork for the use of AI in LLLMs and Visual computing for education, healthcare, and agentic assistive AI for all age groups and needs. It is innovative creators like those at LAION bringing empathy and emotional intelligence to AI that embody the positive social impact that responsible AI can deliver for people.
Intel has a strong commitment to open standards and open-source innovation, particularly in AI, software, and hardware ecosystems, fostering collaboration, accessibility, and interoperability. Intel supports open standards in AI through initiatives like the Linux Foundation's AI & Data projects, ensuring AI frameworks and tools are hardware-agnostic and widely adoptable. This aligns with its Hugging Face collaboration, where Intel optimizes models for ONNX-compatible inference on its hardware. This collaboration goes back to 2021 in order to optimize AI model performance on Intel hardware, focusing on accelerating training and inference for transformer-based models. Their partnership aims to democratize AI by making it faster, more efficient, and accessible through open-source tools.
The mission of Intel's COE with LAION, Germany, established in 2024, is to advance the development of BUD-E, an open-source, empathetic AI education assistant that aims to democratize personalized learning worldwide. LAION is proud to work with Intel, famous for the International Science and Engineering Fair, founded by former Intel CEO Gordon Moore. Hugging Face's Datasets, Models, and Collections are core components of its ecosystem, hosted on the Hugging Face Hub, designed to facilitate AI development and deployment. As further steps, these core components can be enhanced by using Intel-optimized datasets and models, integrated with Intel libraries, and curating collections to showcase these resources for tasks like generative AI or image classification, all aligned with its open-source commitment.
Try Intel's AI Tools
If you'd like to sample the same technological innovations that LAION has access to, give these a try:
See which leading research institutions, universities, and innovative startup companies are joint in efforts just like this as part of the Intel® AI and oneAPI Center of Excellence program.
The Future: Reasoning About Emotions, and the Dawn of Universal Voice Actors
The ability to accurately estimate emotions is a critical first step. The next frontier is to enable AI systems to reason about these emotions in context. We are convinced that in the very near future, foundation models will be multimodal, taking not only text but also audio natively in and natively out. These will be the "universal voice actors" we envision – capable of understanding, embodying, and expressing a vast range of human personas and emotions.
Imagine prompting an AI: "Speak like a caring nurse comforting a worried patient," or "Tell this story as a slightly grumpy but lovable grandpa." LAION's Got Talent and EMONET-VOICE are paving the way for such capabilities. Furthermore, the rich, multi-label, intensity-aware annotations in our EMONET suites provide the kind of data needed for training advanced reasoning models (like OpenAI's O-family or DeepSeek's R1) to understand the implications of emotional states and predict human future actions or outcomes based on observed cues from mental models, moving beyond simple recognition to true comprehension.
To truly democratize this field, LAION, with Intel's support, is committed to annotating millions of permissively licensed audio samples using our EMPATHIC INSIGHT-VOICE model. This will create an unparalleled public resource, fueling further research and development in self-supervised and multi-modal emotion learning.
Looking ahead, our next ambitious goal is to create a massive, permissively licensed multilingual speech dataset exceeding 500,000 hours. This monumental undertaking is powered by the Intel® Tiber AI Cloud, where we are leveraging its high-performance, 192-core CPU instances to process and curate this unparalleled resource. This will further democratize and accelerate research, paving the way for the next generation of emotionally aware AI.
Try It and Collaborate: Join Our Journey
The development of emotionally intelligent AI is a collaborative endeavor. We invite the global AI community – researchers, developers, ethicists, and enthusiasts – to explore our work and contribute to this exciting field.
📚 Read the Papers
- EmoNet Face: https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.20033
- EmoNet Voice: https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.09827
📊 Explore the Datasets
- LAION's Got Talent:
- EMONET-FACE: Collection
- EMONET-VOICE: Collection
🤖 Experiment with the Models
BUD-E Whisper:
Empathic Insight Face:
Empathic Insight Voice:
🌐 Engage with our Community
- GitHub: https://github.com/laion-ai
- Discord: https://discord.gg/xBPBXfcFHd
Stay tuned for the official release of EMONET-VOICE and upcoming publications detailing our methodologies and findings.
Acknowledgements
This ambitious undertaking would not be possible without the incredible support of our partners. We extend our deepest gratitude to the Technical University Darmstadt, DFKI, Hessian AI, TIB-Leibniz Information Centre for Science and Technology, University Hannover, NOUS Research, Camb AI and especially Intel for their indispensable support, resources, and shared vision for advancing open and responsible AI research. Their commitment is instrumental in our journey to create AI that not only understands us but truly cares.