REACHING 80% ZERO-SHOT ACCURACY WITH OPENCLIP: VIT-G/14 TRAINED ON LAION-2B
by: Mitchell Wortsman, 24 Jan, 2023
We have trained a new ViT-G/14 CLIP model with OpenCLIP which achieves 80.1% zero-shot accuracy on ImageNet and 74.9% zero-shot image retrieval (Recall@5) on MS COCO. As of January 2023, this is the best open source CLIP model.
We believe this is interesting because:
- CLIP models are useful for zero-shot classification, retrieval, and for guidance/conditioning in generative models (OpenCLIP is used in Stable Diffusion V2 and currently the third most downloaded model on HuggingFace is a CLIP model). The approach underlying CLIP—self supervised learning on a large, heterogeneous dataset—has been shown to produce models which are more robust and fair.
- Our new ViT-G model achieves the highest zero-shot ImageNet accuracy among models that use only naturally occurring image-text pairs as training data, and without explicit labels, pseudo-labels, or any pretrained image or text encoders.
- Our training run utilized multiple new techniques, including FLIP to accelerate training and model soups to surpass 80% accuracy.
Main Results
The following results are with image resolution 224x224 except for CoCa which uses 576x576.
| Model name | Batch size | Samples seen | Text Params | Image params | ImageNet top1 | Mscoco image retrieval at 5 | Flickr30k image retrieval at 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI CLIP L/14 | 32k | 13B | 123.65M | 303.97M | 75.4% | 61.0% | 87.0% |
| OpenCLIP H/14 | 79k | 32B (16 epochs of laion2B) | 354.0M | 632.08M | 78.0% | 73.4% | 94% |
| OpenCLIP G/14 | 160k | 32B +unmasked fine-tune (details below) | 694.7M | 1844.9M | 80.1%* | 74.9% | 94.9% |
| CoCa | 66k | 33B | 1100M | 1000M | 86.3%** | 74.2 | 95.7 |
* When using CuPL prompts instead of the standard prompts from OpenAI, the zero-shot accuracy is 80.3%. When evaluating at 280x280 and changing resize to squash, Ross Wightman found the model achieves 80.4%.
** In addition to natural language supervision, CoCa uses synthetic captions constructed with the labels from the JFT-3B dataset. In addition to natural language supervision, CoCa uses synthetic captions constructed with the labels from the JFT-3B dataset. 973 of the 1,000 ImageNet classes have a corresponding class in JFT (e.g., see here sec C.7.2).
Also see the figure below (figure code by Ross) and our analysis of scaling trends for OpenCLIP model here.
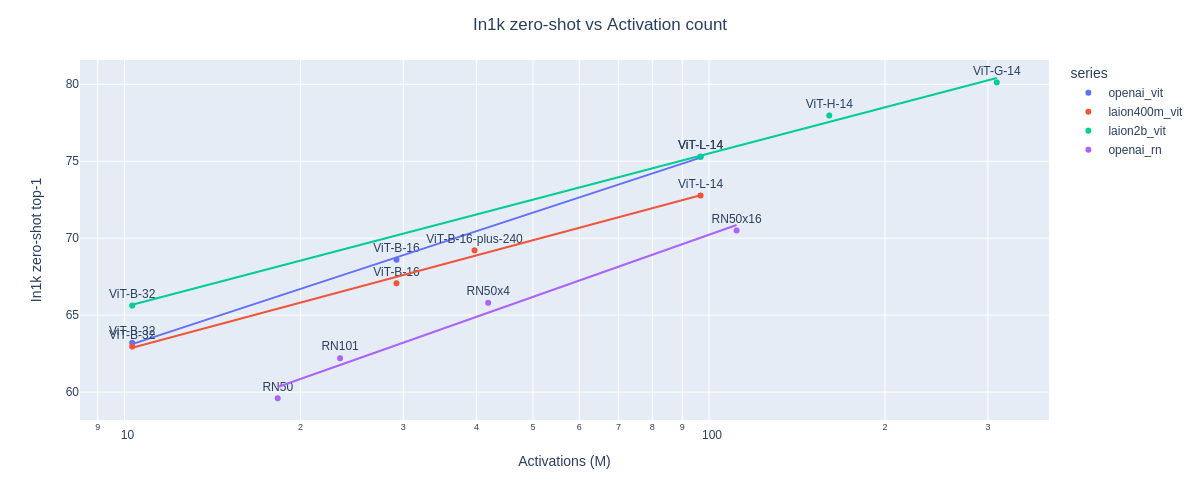
Released Checkpoints
We release the checkpoint through OpenCLIP and in the HuggingFace hub.
Notes on scaling up
To scale up model size while reducing compute we used Fast Language-Image Pre-training (FLIP) with patch dropout 0.5. Similar to Masked Autoencoders (MAE), FLIP drops out patches during training. FLIP also requires a short “unmasked tuning” phase, which we discuss in training notes below. In addition to reducing Giga multiply–accumulate operations (GMACs) for each forward/backward pass, FLIP allowed us to use a larger per-GPU batch size. Without FLIP, gradient accumulation was necessary to maintain a large batch size. Keeping batch size and number of GPUs consistent (at 160k and 512, respectively) but switching to unmasked fine-tuning resulted in a drop from 46.9 to 20.4 samples per second per GPU. For reference, OpenCLIP H/14 with global batch size 79k across 824 GPUs without patch dropout trained at 42 samples/s/GPU.
To scale up the batch size to 160k, we used gradient checkpointing and 80GM VRAM A100s. For the unmasked tuning portion, we also used gradient accumulation (see our implementation for the contrastive objective here). Finally, we used a 2x higher learning rate of 2e-3 compared to our experiments with batch size 80k. The combination of scaling up model, batch size, and learning rate resulted in training instability during the warmup phase. Accordingly, we increased warm-up to 13k steps, trained with layer scale, and used AdamW beta2 0.95. All runs used AMP bfloat16, after previously switching from float16 in prior experiments with L/14 and H/14.
Training notes
Phase 1: Patch dropout
For phase 1 we trained ViT-G with patch dropout 0.5 on LAION-2B for 32B samples seen. We used batch size 160k, learning rate 2e-3, and a cosine decay schedule. After this phase the model reached 79.07 zero-shot top1 accuracy on ImageNet.
Training was mainly done on 512 to 760 A100s depending on availability. When changing the number of GPUs, local batch size was also modified so that the global batch size remained at 160k. When using 512 GPUs we set local batch size to 313 and observed roughly 24k samples per second or 46.9 samples/s/GPU. When using 760 GPUs we set local batch size 211 and observed roughly 33k samples per second or 43.4 samples/s/GPU.
Phase 2: Unmasked tuning + Model soups
For phase 2 we followed FLIP in conducting a short unmasked tuning phase. We fell short of 80% in our first unmasked fine-tuning phase, reaching only 79.43%. So we tried twice more with different settings (described below) to obtain 79.45% and 79.2%, respectively. Next, we followed model soups and averaged the weights of three checkpoints produced by these runs to achieve our final accuracy of 80.1%. LIMoE and PaLI also used model soups for better pre-training.
For our first unmasked fine-tuning run we did not modify the learning rate schedule, but instead doubled the base LR and extended the number of iterations so that the run would proceed for an additional 2B samples seen. LR started at 3.8e-5. For the second run we used LR 5.5e-5 with a full cosine schedule (warmup for roughly 200M samples and a total of 4B samples). The third run had identical hyperparameters to the first but used the LAION-A subset of LAION-2B. LAION-A is a 900M subset of LAION-2B filtered with aesthetic V2 4.5+ and pHash deduplicated. Instead of waiting for the third run to complete we use the checkpoint after approximately 700M samples which, when “souped” with the final checkpoints from the two proceeding runs, already allowed us to surpass our goal of 80% accuracy. This indiviual checkpoint achieved 79.2%.
Unmasked fine-tuning was done on 512 A100 GPUs at a speed of roughly 10,450 samples/s or 20.4 samples/s/GPU.
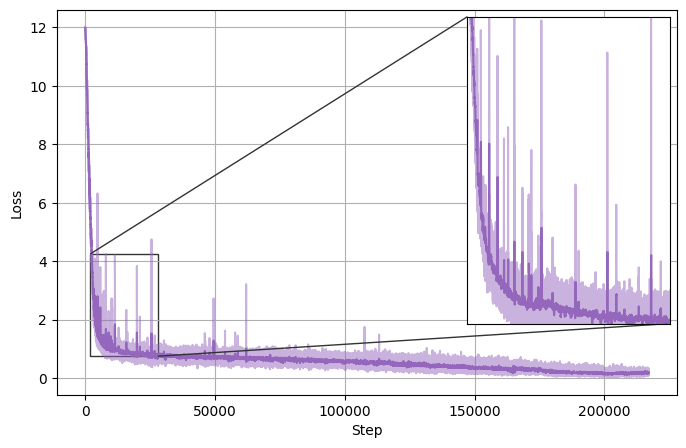
The following plot shows the loss curve for phase 1.
More results
Zero-shot accuracies at resolution 224x224 computed with CLIP Benchmark.
| Dataset | OpenCLIP H/14 | OpenCLIP G/14 |
|---|---|---|
| ImageNet | 78.0 | 80.1 |
| ImageNet-V2 | 70.8 | 73.6 |
| ImageNet-R | 89.3 | 92.1 |
| ImageNet-Sketch | 66.6 | 68.9 |
| ObjectNet | 69.7 | 73.0 |
| ImageNet-A | 59.2 | 69.3 |
| CIFAR-10 | 97.4 | 98.2 |
| CIFAR-100 | 84.7 | 87.5 |
| MNIST | 72.9 | 71.6 |
| SVHN | 56.1 | 62.5 |
| Caltech-101 | 85.0 | 86.4 |
| SUN397 | 75.2 | 74.5 |
| FGVC Aircraft | 42.8 | 49.7 |
| Country211 | 30.0 | 33.8 |
| Cars | 93.5 | 94.6 |
Here is a summary figure comparing G/14 and H/14 made with evals by Romain Beaumont.
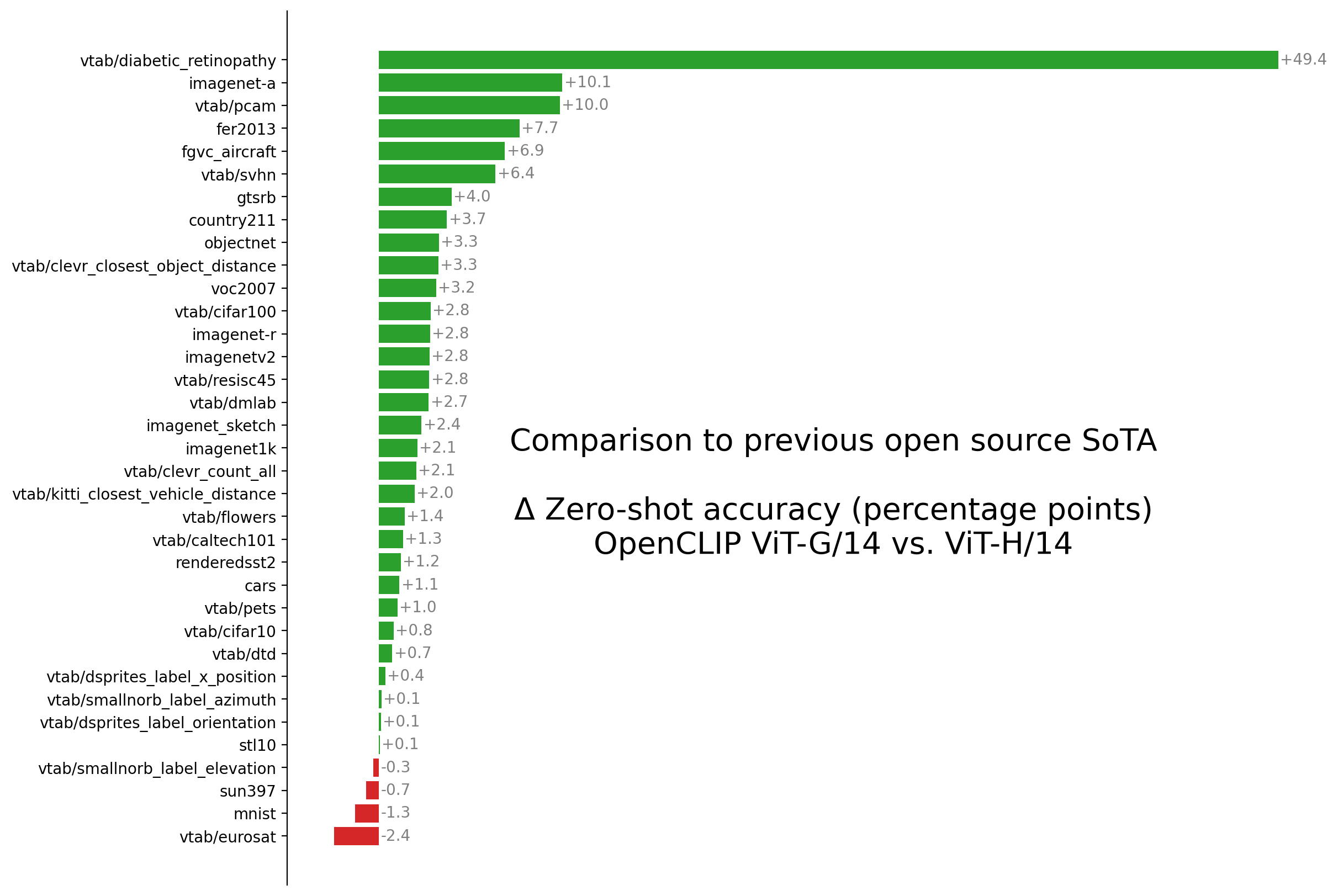
What’s Next?
In the future, we may fine-tune the model to enable multilingual capabilities, or fine-tune at higher resolution. Also, FSDP is coming to OpenCLIP which will allow even larger models, as is CoCa which will allow new openclip models to also be captioners. More contributions to OpenCLIP are always welcome!
Contributions and acknowledgements
Thanks to:
- Romain Beaumont, Ross Wightman, Mehdi Cherti, Gabriel Ilharco, and Jenia Jitsev for providing extensive ideas, advice, engineering support, evaluating the model, and maintaining the openclip repository used for model training.
- Christoph Schuhmann for encouragement and support
- Richard Vencu for cluster support
- Phil Wang and Haoqi Fan for the implementation and discussion regarding patch dropout
- Sho Yaida, Jong Wook Kim, Ari Morcos and Saining Xie for helpful remarks regarding hyperparameters
- Sarah Pratt for implementing CuPL
- Ludwig Schmidt and Ali Farhadi for helpful discussions, and to the RAIVN and EFML labs at the University of Washington
And of course thanks to Emad and Stability AI for providing the compute resources used for these experiments.